Introduction
I have written about why evolution is impossible seven times in the past.[1] Here, I will concentrate on the very mechanism Darwin proposes that drives evolution, which is natural selection.
The full title of Darwin’s Origin of the Species is, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. This, he published in 1859. In it he postulated that all the various forms of life arose from a common organism through a process of gradual change, and he gave no thought as from where, or how this common organism came. The mechanism for driving the changes was natural selection operating on randomly occurring variation. He had observed natural selection taking place with finches on the Galapagos Islands as drought conditions favored finches that had longer and stronger beaks and were thus able to survive by cracking the drought-toughened nuts. By this procedure, he proposed that species evolved from one to another through a series of small changes as each being favored by environmental pressures.
Natural Selection
 Darwin thought that it was natural selection that drove evolution and gave rise to all forms of life. The big problem with this hypothesis is that natural selection although it is real, only selects from what is present already as the name implies, it does not create anything. This fact became apparent in the early years after Darwin’s publication. The modern and revised form of Darwin’s hypothesis is called Neo Darwinism, and this contends that a group of chemicals came together (chemical evolution or abiogenesis) to eventually form themselves into a single-cell species, Darwin’s “common organism” which in turn, evolved into all the forms of life that were ever present.
Darwin thought that it was natural selection that drove evolution and gave rise to all forms of life. The big problem with this hypothesis is that natural selection although it is real, only selects from what is present already as the name implies, it does not create anything. This fact became apparent in the early years after Darwin’s publication. The modern and revised form of Darwin’s hypothesis is called Neo Darwinism, and this contends that a group of chemicals came together (chemical evolution or abiogenesis) to eventually form themselves into a single-cell species, Darwin’s “common organism” which in turn, evolved into all the forms of life that were ever present.
The simplest single cell organism has about 600,000 nucleotides (sometimes referred to as links in a chain) in its genome, whereas a human genome contains more than 3 billion nucleotides. So, to go from molecules to man via single cell species, requires an enormous increase in the genome and the information that it contains. But evolutionists will rarely state it so bluntly or clearly, they prefer to refer to evolution as monkeys to man because it is easier for people to believe.
As stated, natural selection does not add any new genetic information but rather reduces it. By way of explanation, we will look at two examples.
- Consider a group of dogs which consisted of a mixture of dogs with long hair and dogs with short hair. In a severe winter, the short hair dogs would die of cold through lack of thermal insulation because they only have short hair, but the long hair dogs would survive. Hence the genes that code for short hair would be lost from the gene pool of dogs and consequently the gene pool would decrease.
- Bird breeders have taken the green Australian budgerigar, and from it have produced a variety of colours, grey, blue, pink, white etc. This is done by selecting certain genes at the expense of other genes. Ultimately, it is therefore not possible to go back to the original green from any of these other colours because genes have been lost through the selection procedure. The colours which were bred are at the end of the genetic line.
Natural selection is still being pushed as a process of evolution. The following is a Wikipedia statement copied on March 29, 2024.[2]
The evolution of the peppered moth is an evolutionary instance of directional  colour change in the moth population as a consequence of air pollution during the Industrial Revolution. The frequency of dark-coloured moths increased at that time, an example of industrial melanism. Later, when pollution was reduced, the light-coloured form again predominated. Industrial melanism in the peppered moth was an early test of Charles Darwin’s natural selection in action, and it remains a classic example in the teaching of evolution. In 1978, Sewall Wright described it as “the clearest case in which a conspicuous evolutionary process has actually been observed.
colour change in the moth population as a consequence of air pollution during the Industrial Revolution. The frequency of dark-coloured moths increased at that time, an example of industrial melanism. Later, when pollution was reduced, the light-coloured form again predominated. Industrial melanism in the peppered moth was an early test of Charles Darwin’s natural selection in action, and it remains a classic example in the teaching of evolution. In 1978, Sewall Wright described it as “the clearest case in which a conspicuous evolutionary process has actually been observed.
Image credit, Wikipedia commons.
As Wikipedia stated all that is changing is the relative numbers of each of the two peppered moths. No new species have evolved. No evolution has taken place. Peppered moths are still peppered moths.
The following are examples of natural selection that are said to underpin evolution. These have been taken from Wikipedia.
Examples of natural selection in evolution include:
- The evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
- The white fur of arctic animals that helps them blend in with the snow
- The camouflage of grasshoppers and katydids that makes them look like leaves
- The eye-shaped patterns on some butterfly wings that deter predators
- The large throat pouch of pelicans that helps them catch and swallow prey
- The different color of treefrogs that matches their environment
- The long neck of giraffes that allows them to reach higher leaves
In consideration of the first example, further recent research on antibiotic resistance has shown a very small number of bacterial cells mutate in a way that prevents the antibiotic from either entering them or attaching to them, and consequently the antibiotic cannot destroy them. This is described as bacterial cells evolving to become antibiotic resistant. Of course, these resistant bacterial cells will proliferate at the expense of the other cells. But because they are a mutant, they die sooner and are not as vigorous as the natural cells.[3]
The long neck of giraffes
The long neck of giraffes is the actual example that Darwin used, and it was based on his idea, but fallacious, that environmentally caused variations are passed on to succeeding generations. He thus explained the origin of the giraffe’s long neck:
Those individuals, who had some one part or several parts of their bodies rather more elongated than usual, would generally have survived. These will have intercrossed and left offspring, either inheriting the same bodily peculiarities, or with a tendency to vary again in the same manner; whilst the individuals, less favored in the same respects will have been the most liable to perish…. By this process long-continued, which exactly corresponds with what I have called unconscious selection by man, combined no doubt in a most important manner with the inherited effects of the increased use of parts, it seems to me almost certain that an ordinary hoofed quadruped might be converted into a giraffe.[4]
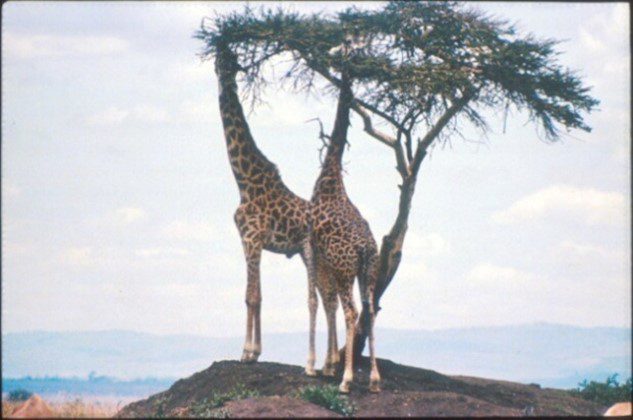 In Darwin’s view giraffes evolved from some horse-like animal that mated with other horse-like animals which happened to have abnormally long necks. This union produced progeny that have even longer necks. This, combined with the fact that that the continued stretching or increase use of parts, stretched their necks and these longer neck species produced progeny with even longer necks and the process was repeated to give giraffes.
In Darwin’s view giraffes evolved from some horse-like animal that mated with other horse-like animals which happened to have abnormally long necks. This union produced progeny that have even longer necks. This, combined with the fact that that the continued stretching or increase use of parts, stretched their necks and these longer neck species produced progeny with even longer necks and the process was repeated to give giraffes.
Giraffes are an excellent example of an animal possessing specific design features. For example, to get blood all the way up its neck to its head, the giraffe has one of the most powerful hearts in the animal kingdom, with double the normal blood pressure. But what happens when the animal lowers its head to drink? With its powerful heart not having to pump against gravity but rather having gravity on its side now, the rush of blood to the giraffe’s brain would render it unconscious. Fortunately, the giraffe has at least three design features that make drinking quite easy.  One is that they splay their front legs, thereby lowering their heart so that the difference between heart and head is not as great. Second, giraffes have a series of one-way check valves in their neck, which prevent a rush of blood when the head is lowered. And the third design feature of giraffes is the ‘wonder net’; a spongy tissue filled with numerous small blood vessels located near the base of the brain. The arterial blood first flows through this net of vessels before it reaches the brain thereby preventing a shock wave of blood hitting its brain. So, when the giraffe finishes its drink, it stands up, the check valves open, the effects of the wonder net and the various counter pressure mechanisms relax, and all is well.
One is that they splay their front legs, thereby lowering their heart so that the difference between heart and head is not as great. Second, giraffes have a series of one-way check valves in their neck, which prevent a rush of blood when the head is lowered. And the third design feature of giraffes is the ‘wonder net’; a spongy tissue filled with numerous small blood vessels located near the base of the brain. The arterial blood first flows through this net of vessels before it reaches the brain thereby preventing a shock wave of blood hitting its brain. So, when the giraffe finishes its drink, it stands up, the check valves open, the effects of the wonder net and the various counter pressure mechanisms relax, and all is well.
Even now, evolutionists still cannot agree on a mechanism by which the giraffe evolved its long neck.[5]
Genetics
 The nineteenth century “Father of Genetics,” Austrian monk Gregor Mendel showed through his experiments with red and white sweet peas, that offspring can only receive what is in their parents’ genes.[6] If for example, the species does not possess the genes for feathers, the progeny will not have feathers. If the species does not have the genes for gills, the progeny will not have gills. Yet Darwin’s theory requires that species gain traits from environmental effects and some other source of genetic novelty such as mutations to change into something else.
The nineteenth century “Father of Genetics,” Austrian monk Gregor Mendel showed through his experiments with red and white sweet peas, that offspring can only receive what is in their parents’ genes.[6] If for example, the species does not possess the genes for feathers, the progeny will not have feathers. If the species does not have the genes for gills, the progeny will not have gills. Yet Darwin’s theory requires that species gain traits from environmental effects and some other source of genetic novelty such as mutations to change into something else.
Having stated that, it needs to be made clear that there is a wide amount of genetic variation within species, as evidenced by the great variety of dogs which originally came from the wolf type, but this occurs as the result of gene shuffling as species breed. Dogs have always been dogs and will remain dogs. But there is a limit to how far these variations can go. For example, when breeders tried to increase the amount of sugar in sugar beet, they were able to increase it from 6 percent to 17 percent and no further, because at that point, they had concentrated all the genes for sugar production into one species.
As an aside, Gregor Mendel showed that what the Bible stated is true, in that every creature was made to reproduce after its kind.[7]
The other examples of natural selection given by Wikipedia are definitely natural selection, but they are not examples of evolution as there is only population changes within the species, and no new species have been created, bears, grasshoppers, butterflies, pelicans, and tree frogs have remained bears, grasshoppers etc.
Mutations
Once mutations of DNA were discovered and understood, evolutionists used it in an attempt to explain how new species could have evolved. But mutations are copying mistakes when DNA is reproduced during cell division. There are at least 5,000 human melodies including Down’s Syndrome, cystic fibrosis, and sickle cell anaemia that are a result of genetic mutations. Instead of mankind evolving onwards and upwards, mutations produce devolution. There are about 100 mutations acquired per generation, and these are building up and this has led many geneticists to state its logical conclusion that we humans are degrading. Geneticists Dr Stanford explains mutations will bring an end to the human race, in this eight-minute video: youtube.com/watch?v=K8KbM-xkfVk.
Conclusion
In his book of 1871, Darwin commented, I had two distinct objects in view, firstly, to shew that species had not been separately created, and secondly, that natural selection had been the chief agent of change, though largely aided by the inherited effects of habit, and slightly by the direct action of the surrounding conditions.[8]
As shown above Darwin failed completely with both of his objectives. Natural selection cannot change one species into another, it cannot change fins into legs or legs into wings. Each has been designed for a particular purpose. The only logical conclusion is that all life was created by a Supernatural Being. Christians believe this Being is the God of the Bible who has contacted us and told us that it was He who brought about creation and we can read about how, why, and in what order He did it in the Bible.
[1] Simply go to “View All Articles in our Blog” on the Home Page.[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peppered_moth_evolution.
[3] https://creation.com/antibiotic-resistance-not-evolution-in-action.
[4] C. Darwin, The Origin of Species, Senate, London, sixth edition, 1872, page 177.
[5] Source: New Scientist web site; Zoologger: How did the giraffe get its long neck? By Michael Marshall, July 7, 2010.
[6] https://www.adefenceofthebible.com/2017/11/15/mendel-verses-darwin.
[7] Gary J Baxter, A Defence of the Bible, third Edition, page 79.
[8] Charles Darwin, The Descent of Man, Volume 1, John Marray London, page 152.

1 Comment. Leave new
Thanks, Gary. I don’t understand a lot of this article but what I do understand makes very, very interesting reading. Thanks again for your trouble in writing all of this!